
The Majestic Green Anaconda: A Guide to the World’s Largest Snake
- Introduction
- Overview of the Green Anaconda
- What are 3 facts about a green anaconda?
- What do Green Anacondas Eat?
- Where Do Green Anacondas Live?
- Are Green Anacondas Venomous?
- Can a Green Anaconda Eat a Human?
- Communication
- Natural history
- Fascinating Facts About Green Anacondas
- FAQs About Green Anacondas
- Conclusion
Introduction
Numerous snakes are found in this advanced age of nowadays. The Anaconda wind is one of them. There are numerous sorts of Anaconda snakes, one of which is the Green Anaconda. These snakes are generally found in the thick timberlands of South America and Trinidad. This wind has colossal quality and is the longest wind among all snakes. The thick and long stature of the Anaconda wind has made its put in the hearts of wind darlings. In today’s article, we will give you with all the data you require around the Anaconda wind.
Overview of the Green Anaconda
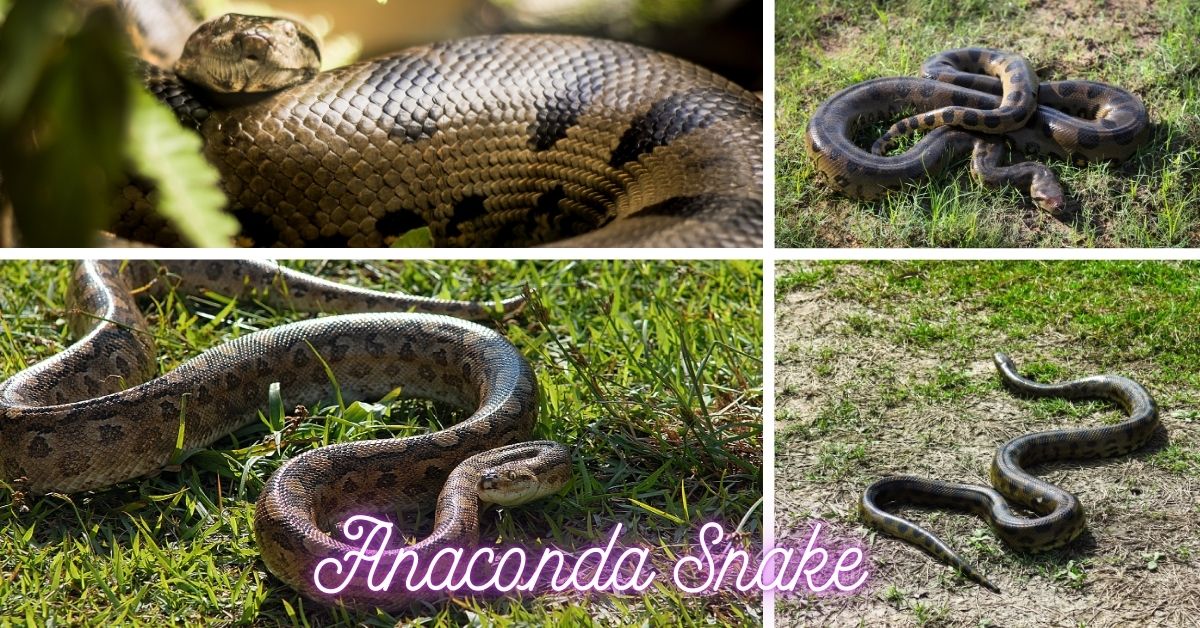
The Green Boa constrictor is the biggest snake species by weight, albeit not the longest, as that qualification has a place with the reticulated python. These snakes can develop to astounding sizes, with females fundamentally bigger than guys. They are principally tracked down in the Amazon Bowl and other freshwater natural surroundings in South America, where they flourish in warm, heat and humidities.
What are 3 facts about a green anaconda?
Surely! The following are three fascinating realities about the green boa constrictor:
- Size and Strength: The green boa constrictor (Eunectes murinus) is one of the biggest and heaviest snake species on the planet. It can arrive at lengths of north of 5 meters (16.4 feet) and weigh in excess of 227 kilograms (500 pounds). This makes it the heaviest snake species by weight, however not really the longest.
- Natural surroundings and Reach: Green boa constrictorsare local to South America, tracked down basically in the Amazon and Orinoco bowls. They possess bogs, swamps, and sluggish streams, leaning toward regions with thick vegetation and water sources. They are fantastic swimmers and invest a lot of their energy in water.
- Taking care of Conduct: Green boa constrictors are strong constrictors, meaning they fold their solid bodies over prey and crush until it chokes. They essentially go after various creatures including fish, birds, vertebrates like capybaras and deer, and even caimans. They are known to trap prey from the water’s edge or strike from submerged.
These realities feature the green boa constrictor’s noteworthy size, specific natural surroundings inclinations, and one of a kind taking care of conduct as a top hunter in its environment.
What do Green Anacondas Eat?
Green boa constrictors are principally rapacious and consume a wide assortment of prey right at home. Their eating regimen regularly incorporates:
- Oceanic Vertebrates: They frequently go after creatures like capybaras, which are huge rodents that possess similar regions as boa constrictors.
- Birds: They may likewise eat birds that draw near striking distance.
- Fish: Being semi-sea-going, fish are a critical piece of their eating routine.
- Reptiles: This can incorporate caimans, other more modest crocodilians, and different snakes.
- Creatures of land and water: Frogs and different creatures of land and water are infrequent prey.
Green boa constrictors are trap hunters, ready to pounce lowered in water, striking quickly to get their prey. They utilize their strong bodies and sharp teeth to limit and consume their casualties.
Where Do Green Anacondas Live?
Green boa constrictors (Eunectes murinus) essentially possess tropical areas of South America, including nations like Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, and a few pieces of Trinidad and the Guianas. They are normally tracked down in swamps, bogs, sluggish streams, and waterways inside rainforests and tropical marshes. These snakes are skilled swimmers and favor sea-going living spaces with thick vegetation where they can snare their prey, which incorporates fish, birds, well evolved creatures, and reptiles.
Are Green Anacondas Venomous?
No, green boa constrictors (Eunectes murinus) are not venomous. They are non-venomous constrictor snakes. Green boa constrictors are among the biggest and heaviest snakes on the planet, essentially tracked down in South America in bogs, swamps, and sluggish streams. They depend on choking to repress their prey, folding over it firmly to choke out it prior to gulping down it. Their amazing size and strength make them imposing hunters in their environment, however they don’t have toxin conveyance frameworks like venomous snakes do.
Can a Green Anaconda Eat a Human?
Indeed, it is hypothetically workable for a Green Boa constrictor (Eunectes murinus) to eat a human, in spite of the fact that it is very uncommon and there are no recorded instances of it occurring in nature. Green Boa constrictors are among the biggest and heaviest snakes on the planet, fit for arriving at lengths of more than 20 feet (6 meters) and gauging a few hundred pounds. They are strong constrictors that fundamentally go after huge creatures like deer, capybaras, and some of the time caimans right at home of the Amazon rainforest.
As far as size and capacity, an enormous Green Boa constrictor might actually overwhelm and endeavor to drink a human, particularly on the off chance that the individual was in or close to water where the boa constrictor is hunting. Nonetheless, because of their regular prey inclinations and the way that human experiences are generally intriguing, such episodes are profoundly improbable.
For security, it’s critical to practice wariness and regard when in regions where Green Boa constrictors are found, but at the same time it’s essential to take note of that they don’t effectively search out people as prey.
Communication
Speaking with green boa constrictors, as with numerous creatures, includes grasping their ways of behaving and regarding their space. Green boa constrictors are fundamentally lone and can be very guarded assuming they feel undermined. Here are a few overall rules for correspondence or collaboration:
- Regard Distance: Boa constrictors are snare hunters and may see unexpected developments or close methodologies as dangers. Keep a conscious separation to try not to stretch the creature.
- Non-verbal communication: Boa constrictors impart through non-verbal communication, for example, murmuring, body stances, and developments. Murmuring is an admonition sign, demonstrating the snake feels compromised or pushed.
- Delicate Methodology: Assuming that you should deal with or move a boa constrictor (under proficient direction), approach smoothly and stay away from unexpected developments. Use gear intended for taking care of snakes to limit pressure.
- Clamors: While not vocal like well evolved creatures, boa constrictors can deliver murmuring sounds as a guarded component. This is their approach to imparting uneasiness or cautioning.
- Visual Signs: Boa constrictors utilize their body to impart. They could loop protectively, level their body to seem bigger, or move away to demonstrate they wish to stay away from a conflict.
- Proficient Direction: Associating with green boa constrictors ought to in a perfect world be finished under the management of experts or specialists in herpetology. They can give experiences into boa constrictor conduct and guarantee security for both the creature and the controller.
Keep in mind, wild creatures, including green boa constrictors, ought to be seen from a deferential distance in their regular territories whenever the situation allows. Understanding their correspondence signals limits pressure and encourages more secure cooperations when vital.
Natural history
The green boa constrictor (Eunectes murinus) is one of the biggest and heaviest snake species on the planet, known for its great size and strong narrowing skills. Here are a few central issues about its normal history:
- Actual Qualities: Green boa constrictors are huge bodied snakes with females essentially bigger than guys. Females can arrive at lengths of north of 20 feet (6 meters) and gauge as much as 550 pounds (250 kilograms), though guys are for the most part more modest, averaging around 10-15 feet (3-4.5 meters) long.
- Territory: They essentially occupy sluggish streams, bogs, and marshes inside tropical rainforests in South America, including the Amazon and Orinoco bowls. They are likewise tracked down in streams, lakes, and overwhelmed regions during the wet season.
- Conduct: Green boa constrictors are semiaquatic, investing quite a bit of their energy in or close to water. They are amazing swimmers and can stay lowered for expanded periods, holding back to trap prey.
- Diet: These snakes are dominant hunters and feed on an assortment of prey, including fish, birds, well evolved creatures (like capybaras, deer, and even pumas), and incidentally different reptiles. They are known for their capacity to consume enormous feasts, on account of their versatile jaws and strong muscles.
- Proliferation: Green boa constrictors are ovoviviparous, meaning females bring forth live youthful. Subsequent to mating, females convey the creating incipient organisms inside their bodies and bring forth 20-40 full grown youthful, which are autonomous from birth.
- Protection: While not right now imperiled, green boa constrictors face dangers like natural surroundings obliteration and chasing after their skin and meat. Preservation endeavors center around safeguarding their wetland natural surroundings and controlling exchange to guarantee economical practices.
- Social Importance: Green boa constrictors have captivated people for quite a long time and component noticeably in nearby legends and fantasies among native South American societies. They have likewise been subjects of logical concentrate because of their noteworthy size and remarkable variations.
Understanding the normal history of the green boa constrictor helps in valuing its job in its environment and the difficulties it faces in nature.
Physical Characteristics
Green Boa constrictors are known for their amazing circumference and solid bodies. They can arrive at lengths of north of 20 feet and gauge as much as 550 pounds or more. Their olive-green shading with dark blotches gives brilliant disguise in their amphibian territories, making them considerable hunters.
Habitat and Behavior
These goliath snakes are semi-sea-going and favor sluggish streams, bogs, and marshes. They are brilliant swimmers and can stay lowered for expanded periods, ready to pounce for their prey, which incorporates fish, birds, vertebrates, and even caimans. In spite of their size, Green Boa constrictors are for the most part not forceful towards people except if incited.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Rearing happens during the stormy season when male boa constrictors will search out females. Subsequent to mating, females bring forth live youthful, which is an uncommon quality among snakes. They can create litters of up to 40 adolescents, every all around 2 feet in length upon entering the world. Youthful boa constrictors develop quickly and are left to fight for themselves from birth.
Conservation Status
Because of natural surroundings misfortune, hunting, and human infringement, Green Boa constrictors face dangers in nature. They are recorded as a types of least worry by the Worldwide Association for Preservation of Nature (IUCN), yet confined declines have been noted. Preservation endeavors center around safeguarding their environments and managing hunting rehearses.
Fascinating Facts About Green Anacondas
- Stomach related Capacities: Boa constrictors are fit for consuming prey a lot bigger than their heads because of their adaptable jaws and expandable stomachs.
- Heat Detecting: They have particular organs on their countenances called “pit organs,” which identify infrared radiation produced by warm-blooded prey, supporting hunting.
- Life span: While definite life expectancies in the wild are muddled, boa constrictors can live for quite a long time in bondage.
Length
The green boa constrictor (Eunectes murinus) is one of the biggest and heaviest snake species on the planet. Grown-up females are regularly bigger than guys. They can arrive at lengths of up to 20 feet (6 meters) and weigh more than 200 pounds (90 kilograms). These estimations make them imposing dominant hunters in their local living space of South America, where they basically possess bogs, swamps, and sluggish streams.
Weight
The heaviness of a green boa constrictor can fluctuate essentially founded on its age, sex, and the accessibility of prey in its natural surroundings. For the most part, grown-up female green boa constrictors are bigger and heavier than guys. All things considered, for certain particularly huge people arriving at loads of north of 300 pounds (136 kilograms).
Diet
Green boa constrictors are enormous, non-venomous snakes found in South America, principally in amphibian conditions like bogs, swamps, and sluggish streams. Their eating routine essentially comprises of:
- Enormous Well evolved creatures: Green boa constrictors are known to go after huge warm blooded animals like capybaras, deer, peccaries, and at times significantly bigger prey like pumas and caimans.
- Sea-going Prey: They likewise consume different amphibian creatures including fish, turtles, birds, and now and again more modest boa constrictors.
- Trap Hunters: Boa constrictors are snare hunters, ready to pounce for their prey to come close prior to striking and choking them.
- Flesh eating Diet: Their eating routine is completely predatory, and they gulp down their prey subsequent to killing it by narrowing.
Green boa constrictors have a mind blowing capacity to consume extremely enormous prey because of their exceptionally flexible skin and solid body, which permits them to stretch to oblige their dinners. They are dominant hunters in their natural surroundings and assume a huge part in controlling prey populaces in their environment.
FAQs About Green Anacondas
Q: How big can Green Anacondas get?
A: Green Boa constrictors can develop to lengths surpassing 20 feet and weigh north of 550 pounds.
Q: Are Green Anacondas dangerous to humans?
Some time strong and skilled hunters, Green Boa constrictors seldom represent a danger to people except if incited or surprised.
Q: Where do Green Anacondas live?
A: They are fundamentally tracked down in the bogs, swamps, and sluggish surges of the Amazon Bowl and different pieces of South America.
Q: What do Green Anacondas eat?
A: They go after various creatures, including fish, birds, vertebrates, and once in a while even caimans.
Q: Are Green Anacondas endangered?
A: Green Anacondas are currently classified as a species of least concern, but face localized threats due to habitat loss and hunting.
Conclusion
The Green Boa constrictor is a really striking animal, both in size and natural significance. As dominant hunters of their environments, they assume a urgent part in keeping up with the equilibrium of their biological systems. While they are not without dangers, proceeded with preservation endeavors are fundamental to guaranteeing these brilliant snakes flourish in the wild for a long time into the future.
All in all, the Green Boa constrictor remains as a demonstration of the wonders of nature and fills in as a sign of the significance of saving biodiversity in our steadily impacting world.




Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for commenting, let me know how I can help you
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you very much sir. Yes sir we have many related content
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your enticle helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.